leetcode hot 100 题解
leetcode hot 100 题解
1. 深度搜索(recursive 解法)
78. 子集
给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。你可以按 任意顺序 返回解集。
示例 1:
1 | |
示例 2:
1 | |
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10-10 <= nums[i] <= 10nums中的所有元素 互不相同
题解:
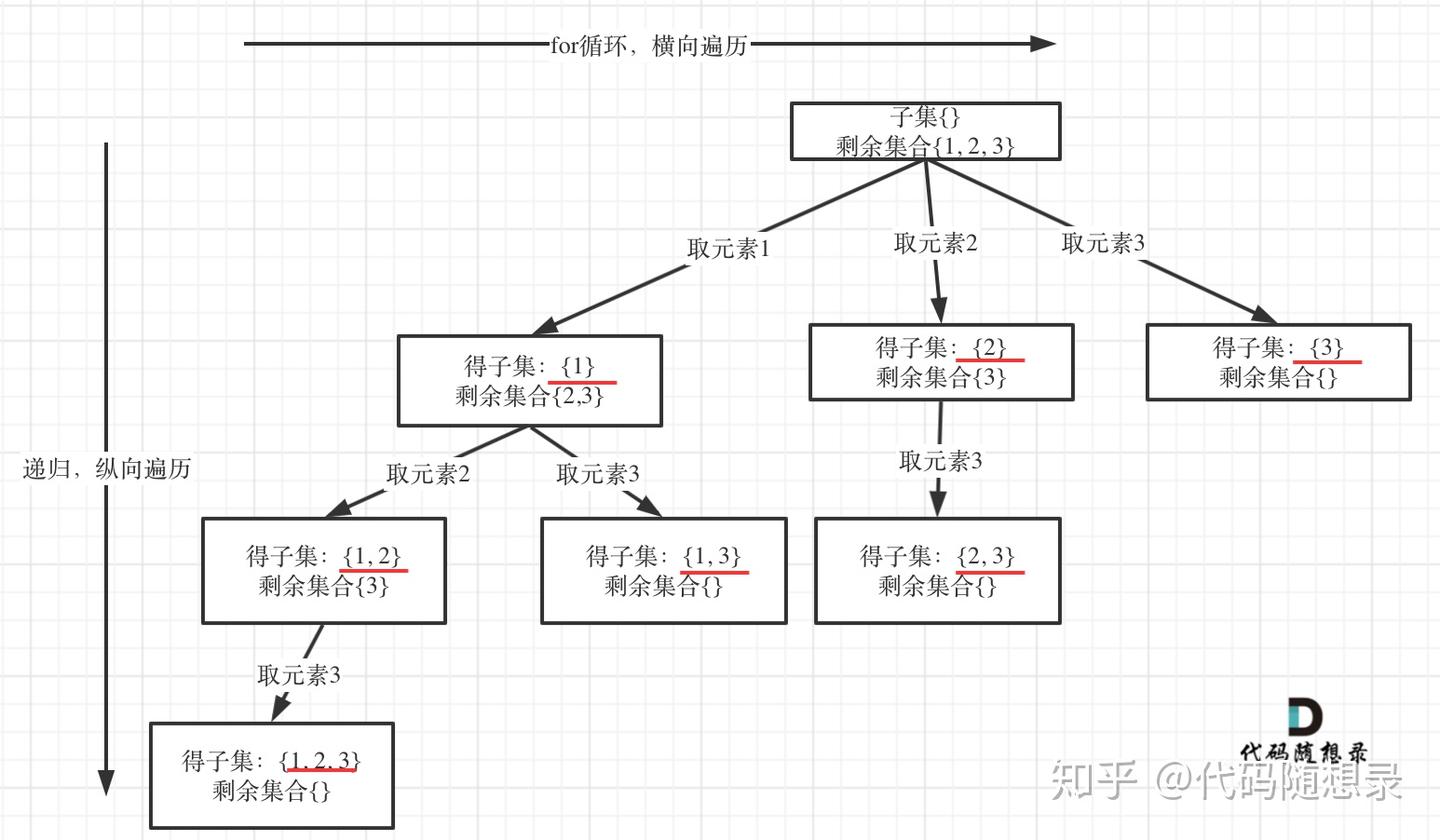
调用:dfs(0, [])
- 得子集:
{} - 剩余集合:
{1,2,3}
- 第一层
for循环
- i=0 → 取元素 1 →
path=[1],进入dfs(1,[1])- 得子集:
{1} - 剩余集合:
{2,3}
- 得子集:
- i=1 → 取元素 2 →
path=[2],进入dfs(2,[2])- 得子集:
{2} - 剩余集合:
{3}
- 得子集:
- i=2 → 取元素 3 →
path=[3],进入dfs(3,[3])- 得子集:
{3} - 剩余集合:
{}
- 得子集:
深入第一条分支(i=0,选了 1)
- 在
dfs(1, [1])里:- for 循环 i=1:取 2 →
path=[1,2]→dfs(2,[1,2])- 得子集:
{1,2} - 剩余集合:
{3} - 再往下,取 3 →
path=[1,2,3]→dfs(3,[1,2,3])- 得子集:
{1,2,3} - 剩余集合:
{}(递归结束)
- 得子集:
- 回溯 pop 掉 3 → 回到
{1,2}
- 得子集:
- for 循环 i=2:取 3 →
path=[1,3]→dfs(3,[1,3])- 得子集:
{1,3} - 剩余集合:
{}
- 得子集:
- for 循环 i=1:取 2 →
下面是回朔具体流程:
1 | |
Python 答案
1 | |
2. 快速选择
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
**题目:**给定整数数组
nums和整数k,请返回数组中第k个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第
k个最大的元素,而不是第k个不同的元素。示例 :
输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4] 和 k = 2
输出: 5
先学一下什么是快速排序(Quicksort)
快速排序的思想其实很简单,就 3 步:
挑一个基准数 (pivot)
- 随便选一个,比如数组第一个或最后一个。
分区 (partition)
- 把比 pivot 小的放一边,比 pivot 大的放另一边。
- pivot 最后就“放到正确的位置上”。
递归左右两边
- 左边继续排,右边继续排。
举个例子:排 [3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4]
- pivot=3
- 比 3 小的:[2,1]
- 比 3 大的:[5,6,4]
- 得到 [2,1] + [3] + [5,6,4]
- 排 [2,1] → 得 [1,2]
- 排 [5,6,4] → 得 [4,5,6]
拼起来 → [1,2,3,4,5,6]
快速选择 (Quickselect)
问题:如果我们只想要「第 k 大元素」,还需要整个数组都排好吗?
👉 不需要!
快速选择就是:
- 用快速排序的分区方法,确定 pivot 的位置。
- 看 pivot 的位置和 k 的关系:
- 如果正好等于 k → 找到了!
- 如果 k 在左边 → 只递归左边。
- 如果 k 在右边 → 只递归右边。
这样就比快排快,因为它只递归 一边。
🌰 举个例子:找 [3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4] 里的第 2 大
数组 [3,2,1,5,6,4],k=2(第二大的数是 5)。
pivot=3 → partition → [5,6,4,3,2,1]
- pivot 的位置是 3(第 4 大)。
- k=2 在左边,所以只递归 [5,6,4]。
子数组 [5,6,4],pivot=5 → partition → [6,5,4]
- pivot 的位置是 1(第 2 大)。
- ✅ 找到了!结果是 5。
时间复杂度
- 每次 partition O(n)
- 但每次只递归一边(大约一半大小)
- 平均复杂度 O(n)
让我们回到这个题 , 根据上面讲的内容,我们需要完成两个函数 , partition 和 select
1 | |
我们在 partition(分区) 时,需要:
- 遍历 [left, right-1],把比 pivot 大的数放到前面。
- 遍历过程中,pivot 不能“碍事”。
- 所以先把 pivot 暂时放到末尾,最后再把它放回正确位置。
store_index 指针指向最左边 left ,然后从左往右遍历把比 pivot大的
1 | |
1 | |
leetcode hot 100 题解
http://example.com/2025/09/23/leetcode hot 100 题解 /